
Jun 18, 2013 · in order to diagnose sinusitis, your orlando ear, nose, and throat doctor (ent) may recommend having x-rays taken. x-rays are a common diagnostic tool for identifying broken bones, which may first come to mind, but it’s also useful in evaluating the possibility of sinusitis.
Opacification Of Maxillary Sinus Answers From Doctors Healthtap
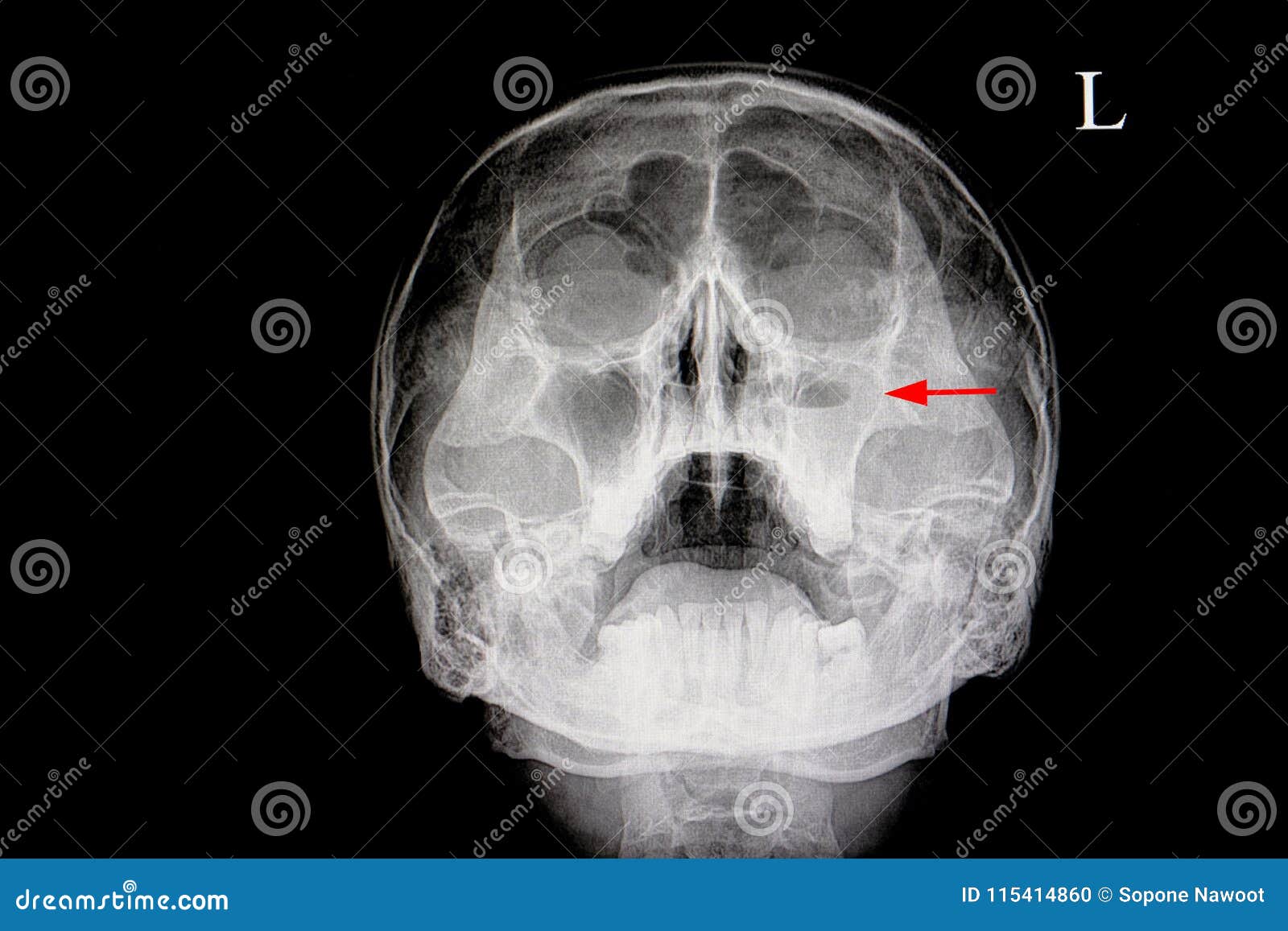
Jan 25, 2017 · maxillary sinusitis is therefore an inflammation of the maxillary sinus. the maxillary sinus (or antrum of highmore) is the largest of your sinuses. once your maxillary sinus is inflamed, it is possible for the infection to then spread to the orbit or to the ethmoid sinus. the maxillary sinus is incredibly close to the maxillary teeth. sinus maxillary sinusitis x ray X-ray film of the face frontal, nose-chin and lateral projection. volume formation of the right maxillary sinus. marker. negativ. a images of the x-ray face.
The radiographic maxillary sinus findings were categorized as: (1) no sign of pathology, (2) mucosal thickening, (3) mucous cyst, or (4) occupation of the entire sinus. As you're sitting in the dentist's chair, you might be told you need a dental x-ray. here's what to expect with this painless procedure and why your dentist may recommend it. Mar 29, 2020 · a sinus x-ray helps doctors detect problems with the sinuses. sinuses are normally filled with air, so the passages will appear black on an x-ray of healthy sinuses. a gray or white area on an.
Radiologic Imaging In The Management Of Sinusitis American
The radiographic maxillary sinus findings were categorized as: (1) no sign of pathology, (2) mucosal thickening, (tiga) mucous cyst, or (4) occupation of the entire sinus. Maxillary antrostomy is the most common method for performing endoscopic sinus surgery. it involves enlarging the maxillary sinus opening. benjamin f. asher, md, is a board-certified otolaryngologist. he has a private practice in new york c. Imaging findings are nonspecific and can be seen in a large number of asymptomatic patients (up to 40%) 11. imaging findings should be interpreted with clinical and/or endoscopic findings. a gas-fluid level is the most typical imaging finding. however, it is only present in 25-50% of patients with acute sinusitis 4. opacification of the sinuses and gas-fluid level best seen in the maxillary sinus. it does not allow assessment of the extent of the inflammation and its complications. the most common method of evaluation. better anatomical delineation and assessment of inflammation extension, causes, and complications. peripheral mucosal thickening, gas-fluid level in the paranasal sinuses, gas bubbles within the fluid and obstruction of the ostiomeatal complexesare recognized findings. rhinitis, often associated with sinusitis, is often characterized by thickening of the turbinates with obliteration of the surrounding air channels. this should not be confused with the normal nasal cyc The main principle of determining the appearance of this disease is a pure accident, in which the patient falls ill with the usual sinusitis and goes to x-ray. and only then does the x-ray show that the sinus walls are not as they should be and there is a certain bulge.
Maxillary Sinusitis Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
Early duduk perkara signs: a sinus on sinus maxillary sinusitis x ray x-ray should appear black,. opacification will appear white or grey. this could be fluid, polyps or inflammation of the the mucosal membr. A sinus x-ray is an imaging test that uses x-rays to look at your sinuses. the sinuses are air-filled pockets (cavities) near your nasal passage. we are experiencing extremely high call volume related to covid-19 vaccine interest. please un.
An x-ray of the sinuses was formerly the standard method of diagnosing acute sinusitis in the sinuses behind the cheeks (maxillary sinuses) or behind the eyebrows (frontal sinuses). because a computed tomography (ct) scan shows a much clearer picture of the sinuses and other structures, the use of standard x-rays has declined. Fever, headache, postnasal discharge of thick sputum, nasal congestion and an abnormal sense of smell. acute sinusitis is a clinical penaksiran characterized by symptom duration of less than 4 weeks 11. Acute sinusitis (rare plural: sinusitides) is an acute inflammation of the paranasal sinus mucosa that lasts less than four weeks and can occur in any of the paranasal sinuses. if the nasal cavity mucosa is also involved then the term rhinosinusi.
Conservative medical treatment until the inflammation subsides and treatment of the cause, e. g. dental caries. if it becomes chronic sinusitis, functional endoscopic sinus surgerymay be considered. 1. erosion through bone 1. 1. subperiosteal abscess 1. 1. 1. frontal sinus superficially (pott puffy tumor) 1. 1. 2. frontal or ethmoidal sinuses into the orbit (subperiosteal abscess of the orbit) dua. sinus maxillary sinusitis x ray dural venous sinus thrombosis tiga. intracranial extension 3. 1. meningitis tiga. dua. subdural empyema tiga. tiga. cerebral abscess. Learn what you need to know about dental x-rays, including how often you should get them, descriptions of different types, and what they are used for. edmund khoo, dds, is board-certified in orthodontics and is a diplomate of the american b.
Cyst Of Maxillary Sinus Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment
You’ve probably put on a lead apron before during x-rays to protect your penting organs, but did you know that you can request a thyroid guard? sometimes it’s on the apron already, but doctor’s simply don’t flip it up to cover your neck. wome. Usually following a viral upper respiratory tract infection. dental caries, periapical abscess and oroantral fistulation lead to a spread of infection to the maxillary sinus. cystic fibrosisand allergy are risk factors. other anatomical variants that may predispose to the inflammation include nasal septal deviation, a spur of the nasal septum and/or frontoethmoidal recess variants. patients in an intensive care setting are at an increased risk of acute sinusitis. risk factors identified include 10: 1. indwelling nasogastric tubes and/or endotracheal tubes 1. 1. especially nasotracheal sinus maxillary sinusitis x ray routing 2. prolonged duration on the unit 3. younger age. X-rays use beams of energy that pass through body tissues onto a special film and make a picture. they show pictures of your internal tissues, bones, and organs. bone and metal show up as white on x-rays. x-rays of the belly may be done to.
See full list on radiopaedia. org. See full list on radiopaedia. org. Nov 15, 2002 · plain radiography has a limited role in the management of sinusitis. although air-fluid levels and complete opacification of a sinus are more specific for sinusitis, they are only seen in 60. Plain radiography has a limited role in the management of sinusitis. although air-fluid levels and complete opacification of a sinus are more specific for sinusitis, they sinus maxillary sinusitis x ray are only seen in 60.
Sinus x-ray: purpose, procedure, and risks.
A sinus x-ray (or sinus series) is an imaging test that uses a small amount of radiation to visualize details of your sinuses. sinuses are paired (right and left) air-filled pockets that. Case of maxillary sinusitis (acute on chronic). x-ray skull is not routinely carried out nowadays after the advancements in ct. ct pns is usually advised for evaluation of paranasal sinuses. 1 article features images from this case. The maxillary sinus (or antrum of highmore) is the largest of your sinuses. once your maxillary sinus is inflamed, it is possible for the infection to then spread to the orbit or to the ethmoid sinus. the maxillary sinus is incredibly close to the maxillary teeth. in fact, it can often be seen on a dental x-ray situated above the molar and pre.
Posting Komentar untuk "Sinus Maxillary Sinusitis X Ray"